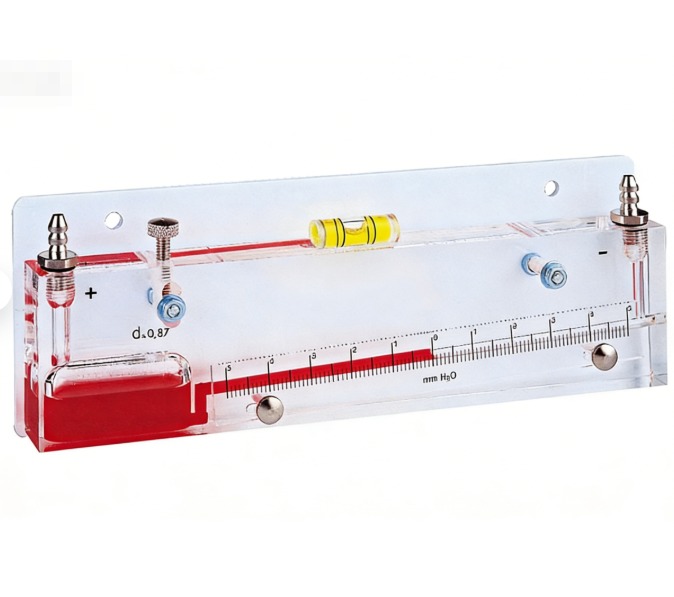
This high-precision mechanical differential pressure measuring instrument. With its transparent design, precise leveling and zeroing mechanism, and portability, it has become a professional measurement tool in fields such as HVAC and cleanroom environmental control. The advantage of the product lies in its extremely high sensitivity measurement without the need for a power supply, and its flexible and convenient use in the workplace. Inclined Liquid Column Manometers is a critical diagnostic tool for HVAC engineers, cleanroom commissioning personnel, building energy auditors, and industrial process control technicians. Because this product can measure the unit of millimeter water column and a small range of around ± 5, quantifying subtle changes in air pressure that cannot be detected by the naked eye. So it plays an important core role in measuring ventilation, airflow, and microenvironment pressure control.
We need to first understand the “triangular relationship” between range, working fluid, and angle. These three factors are closely related and together determine the final measured performance:
Target assumption: Measure smaller pressure → Use lighter working fluid (e.g. d=0.78) and/or smaller tilt angle (e.g. 15 °).
Objective assumption: Measuring greater pressure requires the use of heavier working fluid (such as water, d=1.0) and/or larger tilt angles (such as 60 ° or even 90 ° perpendicular).
Firstly, it is necessary to determine which industry to measure? First estimate the pressure value, as different industries use different pressure values:
How to choose the correct range?
Clean room pressure difference: usually 5-20 Pa
Ordinary air-conditioned room pressure difference: about 5-15 Pa
Fresh air filter (initial effect): final resistance of about 50-100 Pa
Medium efficiency filter: final resistance of about 100-250 Pa
Static pressure inside the air duct: Low speed air ducts are approximately 30-100 Pa, while high-speed air ducts may exceed 200 Pa
Then follow the “1.5 times principle” (x1.5)
The selected range should be slightly larger than your estimated maximum pressure value, usually around 1.5 times the estimated value. For example, when measuring a pressure difference of about 15 Pa in a clean room, choosing a range of 0-25 Pa is the most suitable, which can ensure accuracy and not exceed the range.
Regarding the confirmation of scale units, different industries use different pressure scales.
Millimeter water column is a traditional and intuitive unit commonly used in the HVAC field.
Pascal is an international standard unit that is more universal.
Conversion relationship: 1 mmH ₂ O ≈ 9.8 Pa. For ease of calculation, it is often approximated as 10 Pa in engineering.
Below is a table summarizing the mainstream ranges of Inclined Liquid Column Manometers, along with their common parameter combinations and typical applications.
| Typical range (Pa) | Typical range(mmH₂O) | Common working fluid specific gravity (d) | Common inclination angle | Characteristics and Typical Applications |
| 0-15 Pa | 0-1.5 | 0.78, 0.83 | 15°, 30° | The measurement sensitivity is the highest. Used for precise monitoring of extremely low pressure differentials in high-end cleanrooms (such as ISO level 5), biosafety cabinets, etc |
| 0-25 Pa | 0-2.5 | 0.87 | 30° | Standard range for positive and negative pressure control in cleanrooms and laboratories |
0-50 Pa | 0-5 | 0.87 | 30°, 45° | The most commonly used ranges for HVAC debugging. Suitable for measuring room pressure difference and low wind speed and pressure. |
| 0-100 Pa | 0-10 | 0.87, 0.79 (alcohol) | 45°, 60° | The most widely used universal range. Covering most of the filter pressure drop and ventilation duct static pressure measurement. |
| 0-250 Pa | 0-25 | 1.0 (water), 0.79 | 60°, 90°(vertical) | Used for measuring high wind speed dynamic pressure, fan outlet residual pressure, and industrial ventilation systems. |
| 0-500 Pa | 0-50 | 1.0 (water) | 90°(vertical) | Approaching the upper limit of the range of a micro pressure gauge, used for industrial applications or teaching demonstrations with large pressure differentials. |
Summary and Suggestions:
For the vast majority of HVAC debugging and cleanroom monitoring, the two ranges of 0-25 Pa and 0-50/100 Pa are the most frequently used choices for instruments.
If your job involves multiple differential pressure measurements (such as measuring both room differential pressure and filter resistance), investing in a multi angle adjustable and multi range model would be the most cost-effective choice.
The most important point is to confirm that the specific gravity (d value) of the instrument’s working fluid matches the scale when purchasing, and the working fluid cannot be changed arbitrarily.